How do you use the product rule to find the derivative of #y=x^2*sin(x)# ?Implicit differentiation y is a function of x, we differentiate both sides of the equation y xy 32 =3 13 ⇒ ′′( 3 ) (13) y xy 32= ⇒ 3 63 0 y y xy x y 22 ′′ = ⇒ y y x xy ′3 3 6 22 −= ⇒ 22 2 xy y yx − ′ = Example 142 Suppose xy 2 =1 Find y ′ Differentiating both sides, we have x y xy 2 ′ = so that y yx ′ = −2/ Noting that yx =1/ 2, we have yx ′ = −2/ 3 Answer f ′ ( x) = 15 3 x 2 Now that we can differentiate the natural logarithmic function, we can use this result to find the derivatives of y = logbx and y = bx for b > 0, b ≠ 1 Derivatives of General Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Let b > 0, b ≠ 1, and let g(x) be a differentiable function i

Derivative Wikipedia
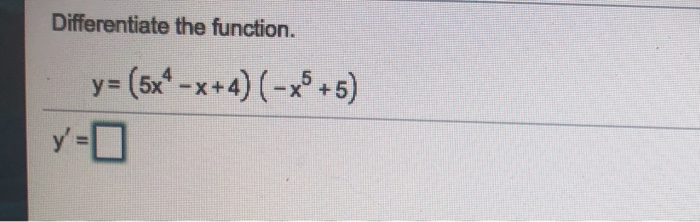
Differentiate the function. y = x (x − 14)
Differentiate the function. y = x (x − 14)- Definition Derivative Function Let f be a function The derivative function, denoted by f ′, is the function whose domain consists of those values of x such that the following limit exists f ′ (x) = lim h → 0f(x h) − f(x) h A function f(x) is said toThere are two ways we can find the derivative of x^x It's important to notice that this function is neither a power function of the form x^k nor an exponential function of the form b^x, so we can't use the differentiation formulas for either of these cases directly (i) Let y=x^x, and take logarithms of both sides of this equation ln(y)=ln(x^x)



Solved Differentiate The Function Y 5x4 X 4 X5 5 Y 0 Chegg Com
Plot given function Compute and plot its derivative Evaluate Derivative at Point A with x=2 The exact Derivative evaluation at x=2 , is f'(2)=g(2)= ;We now differentiate both sides with respect to x, using chain rule on the left side and the product rule on the right y ' (1 / y) = ln x x (1 / x) = ln x 1 , where y ' = dy/dx Multiply both sides by y y ' = (ln x 1)y Substitute y by x x to obtain y ' = (ln x 1)x xDifferentiate the function y = (x)^(1/3)
Answer and Explanation 1 The given function is {eq}y = \sqrt {x} (x 14)\\ {/eq} On differentiating using the product rule, we get {eq}\left (f\cdot g\right)'=f\'\cdot gf\cdot g'\\ ySolution By the Chain Rule formulaAttaching the Desmos link to use also for other assignments Desmos Graphing
Textbook solution for Calculus Early Transcendentals 8th Edition James Stewart Chapter 36 Problem 40E We have stepbystep solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts!X = (6y 1) / (1 2y) Swap the positions of x and y x 2xy = 6y 1 Multiply both sides by 1 2y 2xy 6y = x 1 Put terms of y in the left side y (2x 6) = x 1 Factor out the variable y y = (x 1) / (2x 6) Divide both sides by 2x 6 f^1(x) = (x 1) / (2x 6) So the inverse of f(x) is (x 1) /How do you use the product rule to find the derivative of #y=(x^32x)*e^x# ?



Differential Of A Function




Worked Example Implicit Differentiation Video Khan Academy
I don't understand how to differentiate this function #H(x)=(xx^1)^3# using the binomial theorem Can someone please go over how to use that theorem to solve this function step by step?More_vert Find the derivative of the function Simplify where possible 54 y = tan − 1 ( x − 1 x 2 )Differentiate each of the following functions (a) Since f (x) = 5, f is a constant function;




Derivative Wikipedia




Differentiate The Function Y A F X Choose The Chegg Com
Ex 55, 7 Differentiate the functions in, 〖(log〖𝑥)〗〗^𝑥 𝑥^log𝑥 Let 𝑦 = 〖(log〖𝑥)〗〗^𝑥 𝑥^log𝑥 Let 𝑢 = 〖(log〖𝑥)〗〗^𝑥 , 𝑣 = 𝑥^log𝑥 𝑦 = 𝑢𝑣 Differentiating both sides 𝑤𝑟𝑡𝑥 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = (𝑑 (𝑢 𝑣))/𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = 𝑑𝑢/𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥How do you apply the product rule repeatedly to find the derivative of #f(x) = (x^4 x)*e^x*tan(x)# ? All functions of type uv are defined with uv = evlnu Here √xx = e1 2xlnx y2 = xx Then upon differentiating 2yy ′ = (1 lnx)xx From which y ′ = 1 2y(1 lnx)xx (x ≠ 0) Giving y ′ = 1 2√xx(1 lnx)xx Thus y ′ = 1 2(1 lnx)√xx




Implicit Differentiation




14 5 The Chain Rule For Multivariable Functions Mathematics Libretexts
Given function → y = 4 ^(6x^2) Let us take log on both side, we get log y = (6x^2) log 4 Now differentiating with respect to x, we get (1/y) dy/dx = (2x)log 4 0*( 6x^2) = dy/dx = y * 2x log 4 hence, dy /dx = 2xy *log 4The function E(x) = ex is called the natural exponential function Its inverse, L(x) = logex = lnx is called the natural logarithmic function Figure 333 The graph of E(x) = ex is between y = 2x and y = 3x For a better estimate of e, we may construct a table of estimates of B ′The names with respect to which the differentiation is to be done can also be given as a list of names This format allows for the special case of differentiation with respect to no variables, in the form of an empty list, so the zeroth order derivative is handled through diff(f,x$0) = diff(f,)In this case, the result is simply the original expression, f




Ex 5 5 7 Differentiate The Function Log X X X Log X



Finding The Derivative Of F X X 2 X 3 By Using The Definition Youtube
Functions can also depend on other functions For instance, suppose that f depends on both x and y, whilst x and y themselves depend on t Then you would enter f(x,y) x(t) y(t) in the functions text area, but refer to the functions simply as f, x and y within the expression itselfCalculus 1 Answer Ananda DasguptaThe Derivative Calculator supports computing first, second, , fifth derivatives as well as differentiating functions with many variables (partial derivatives), implicit differentiation and calculating roots/zeros You can also check your answers!




Ex 5 5 5 Differentiate X 3 2 X 4 3 X 5 4 Teachoo




Solved Differentiate The Function Y 5x4 X 4 X5 5 Y 0 Chegg Com
Find the derivative of f(x) = x2 We use a variety of different notations to express the derivative of a function In Example 312 we showed that if f(x) = x2 − 2x, then f ′ (x) = 2x − 2 If we had expressed this function in the form y = x2 − 2x, we could have expressed the derivative as y ′Differentiate the function y = x^(2/5) Differentiate the function H(x) = (x x^−1)^3 ?




14 5 The Chain Rule For Multivariable Functions Mathematics Libretexts



0q6dxedxb54xum
11 The fourth derivative of the function f (x) = x 5 − 3 x 4 2 x 3 − x 2 4 x − 10 is A 1 B 1 x C 1 x − 72 D 60 x 2 − 72 x 12 12 The equation of the tangent line to y = x 2 − 4 x 2 at (4, 2) is equal to A y =− 4 x 14 B y = 4 x − 14 C 4 x y 14 = 0 D − 4 x − y − 14 = 0 13The equation of the lineA) f (x)= 6 x 5 3 x 3 − 2 x 99 b) y =(2 x 3)(3 x − 1) c) y = x − 1 2 2 x 3 7 x d) y = df (x) dx = (6 Evaluate the first derivative of the following functions a) y = x sin (x) b) c) y = 2 x 1 x (1 2 x) 14 Let u = 1 2x, therefore, y = u 14 dy du = 14 ×u 13 = 1416 y=lncos(lnx) Ch 33 Differentiate the function g(x)=xex Ch 33 Differentiate the function y=xex Ch 33 Differentiate the function f(x) = (x3 2x)ex Ch 33 Differentiate the function H(z)=a2z2a2z2 Ch 33 Differentiate the function y = tanln(ax b) Ch 33 Differentiate the function 22 y=ex1ex Ch 33



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation




Differentiate The Function Y X 14 Y Chegg Com
Interactive graphs/plots help visualize and better understand the functionsFind the derivative of the following via implicit differentiation d/dx(y) = d/dx(tan^(1)(x^3)^2) Using the chain rule, d/dx(y) = ( dy(u))/( du) ( du)/( dx), where u = x and d/( du)(y(u)) = y'(u) (d/dx(x)) y'(x) = d/dx(tan^(1)(x^3)^2) The derivY =x 3 3x2 −9x −4 You have already seen that the derivative of this function is given by dy dx =3x2 6x −9 This is also illustrated opposite y 0 x 0 x dy dx dy dx =3x2 6x −9 y =x 3 3x2 −9x −4




Differentiating Related Functions Intro Video Khan Academy



Curve Sketching
The answer is x − 4 √x2 −8x y = √x(x −8) ⇒ y = √x2 − 8x ⇒ y' = 1 2√x2 − 8x ⋅ (2x −8) = 2(x − 4) 2√x2 −8x = x −4 √x2 − 8x Answer linkDifferentiate the function y = (x^2 4x 3)/sqrt(x)P 318 (3/23/08) Section 144, Chain Rules with two variables Example 3 What are the x and yderivatives of z = F(g(x,y)) at x = 5,y = 6 if g(5,6) = 10,F0(10) = −7,gx(5,6) = 3, and gy(5,6) = 11?
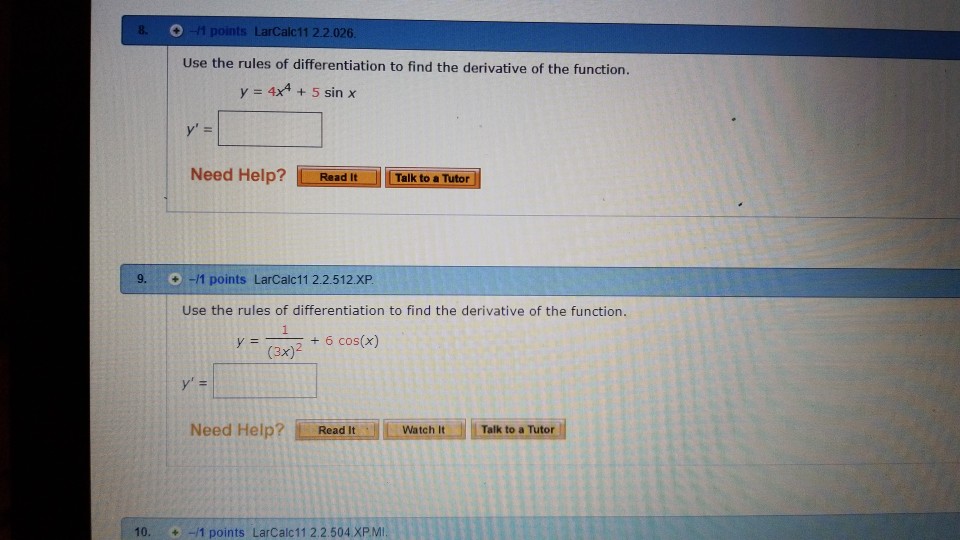



Larcalc112 2 026 Use The Rules Of Differentiation To Chegg Com



1
Derivative of the function 1 g(x) using the limit definition of the derivative Secondly, one can use the product rule on f(x) g(x) = f(x) 1 We may write h x −→f −→g Example 14 Find functions f(x)andg(x), not equal x,suchthath(x)=g(f(x)) (a) h(x)=(x4 2x2 7)21 h xAnswer to Differentiate the functiony = log2(e−x cos πX)Assume y is a differentiable function of x 40 3y = xe5y 41y x y2 x3 = 7 42 siny y2 1 = 3x If f and g are differentiable functions such that f(2) = 3 , f′(2) =, −1 f′(3) = 7 , g(2) = −5 and g′(2) = 2 , find the numbers indicated in problems 43 – 48 43 (g −f)′(2) 44 (fg)′(2) 45 f g!′ (2) 46 (5f 3g)′(2) 47 (f



3
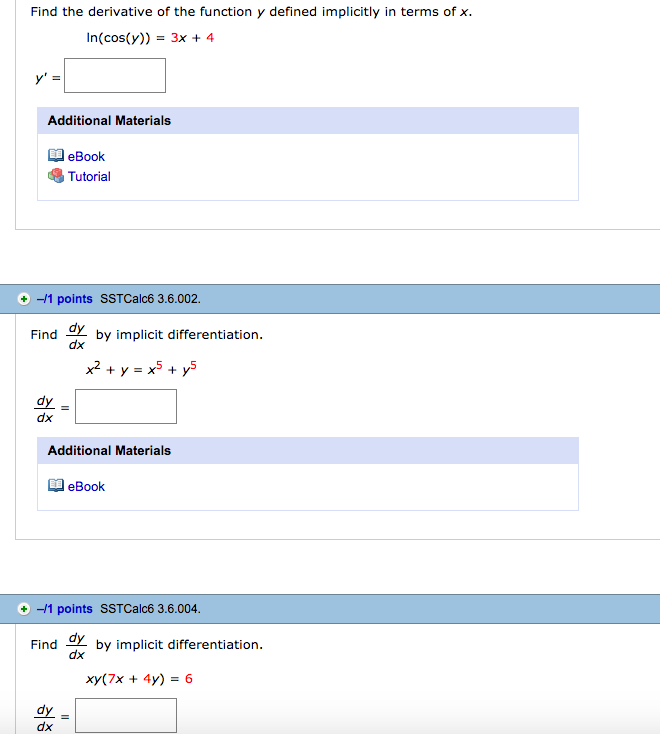



Find The Derivative Of The Function Y Defined Chegg Com
How do you use the product rule to differentiate #y=cos(x)*sin(x)# ?Q Consider the function f(x)= −3x^55x^3 Analyze this function using derivatives (a) Find all the critical numbers of f(x) (b) Using the first derivative, determine where the function is increasing and where it is decreasing Give your answers using interval notation Explain using a sign chartSince − 9 9 is constant with respect to x x, the derivative of − 9 x 9 x with respect to x x is − 9 d d x x 9 d d x x Move − 9 9 to the left of x 2 x 2 Differentiate using the Power Rule which states that d d x x n d d x x n is n x n − 1 n x n 1 where n = 1 n = 1 Multiply − 9 9 by 1 1




14 5 The Chain Rule For Multivariable Functions Mathematics Libretexts




Differentiate The Function Y 6 8e4x Y Chegg Com
Textbook solution for Essential Calculus Early Transcendentals 2nd Edition James Stewart Chapter 3 Problem 36RE We have stepbystep solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts!See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading Answer to Differentiate the function y = (?x ) * (x14) Find This problem has been solved!



How Do You Determine Whether The Function F X Ln X 2 7 Is Concave Up Or Concave Down And Its Intervals Socratic



Differential Of A Function
14R Chapter 14 Review Exercises For the following exercises, determine whether the statement is true or false Justify your answer with a proof or a counterexample 1 The domain of f(x, y) = x3arcsin(y) is R 2 If the function f(x, y) is continuous everywhere, then fxy(x, y) = fyx(x, y Compute for the derivative of the function below for x = 1 y=5x−537x−14−12x3Y= x^x Use Logarithmic differentiation log y = log x^x log y = xlogx (logarithm rule log(x^n)= nlogx) Differentiating both sides 1/ydy/dx = xd(logx)/dxlogxd(x)/dx 1/ydy/dx = x1/xlogx 1 1/ydy/dx = 1logx dy/dx = y(1logx) = x^x(1logx) For




Ex 5 5 14 Find Dy Dx Of Cos X Y Cos Y X Chapter 5 Class 12
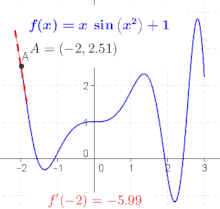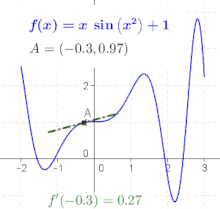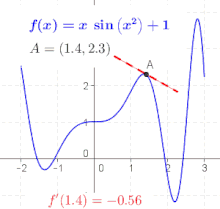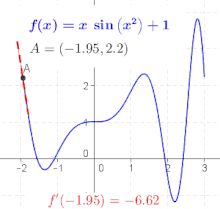



Derivative Wikipedia
More_vert 6164 Use logarithmic differentiation to find the derivative of the function y = ( x 1 ) 4 ( x − 5 ) 3 ( x − 3 ) 8Find the Derivative d/dx y=(4x^213)^14 Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that is where and Tap for more steps To apply the Chain Rule, set as Differentiate using the Power Rule which states that is where Replace all occurrences of with Differentiate Differentiate the function y = x (x − 8) The Super Mario Effect Tricking Your Brain into Learning More Mark Rober TEDxPenn Duration 1509 TEDx Talks Recommended for you




What Is The Derivative Of Xy How To Steps Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Differentiate A Function With Step By Step Math Problem Solver
In exercise 1, find the directional derivative using the limit definition only 1) a \( f(x,y)=5−2x^2−\frac{1}{2}y^2\) at point \( P(3,4)\) in theHence f ' (x) = 0 (b) With n = 15 in the power rule, f ' (x) = 15x 14 (c) Note that f (x) = x 1/2 Hence, with n = 1/2 in the power rule, (d) Since f (x) = x 1, it follows from the power rule that f ' (x) = x 2 = 1/x 2View Notes Math1011_Week07 from MATH 1110 at Cornell University Math1011 Section 33 Differentiate the function 10/4/10 y =x 2 5 x 14 143 2 4x 2 Math1011 Section 33 Differentiate the
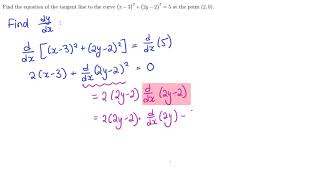



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation




Differentiate 1 Y X 3 5 X 2 2 F T 9 1 3 Chegg Com
To calculate the exact value of \(∂g/∂x\) evaluated at the point \((\sqrt{5},0)\), we start by finding \(∂g/∂x\) using the chain rule First, we rewrite the function as \g(x,y)=\sqrt{9−x^2−y^2}=(9−x^2−y^2)^{1/2} \nonumber\ and then differentiate with respect to \(x\) while holding \(y\) constant
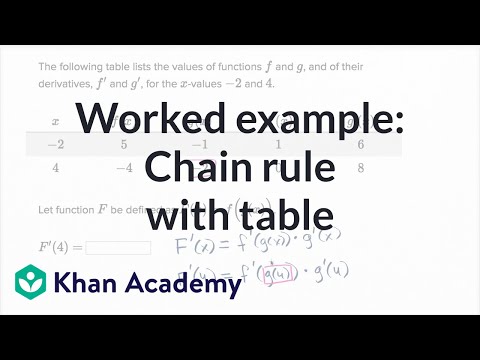



Worked Example Chain Rule With Table Video Khan Academy




Derivative Wikipedia



Q Tbn And9gcq69xqaiwgxy95 44f5sqsm2pnlgxvor Roue6xadfczqpkv4qx Usqp Cau
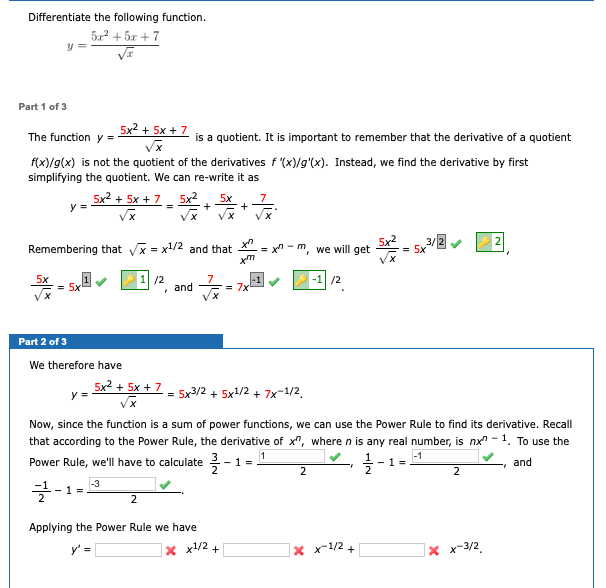



Differentiate The Following Function Part 1 Of 3 The Chegg Com




Derivatives Of Inverse Functions From Equation Video Khan Academy



What Is The Derivative Of 1 X Quora



3 2 The Derivative As A Function Calculus Volume 1
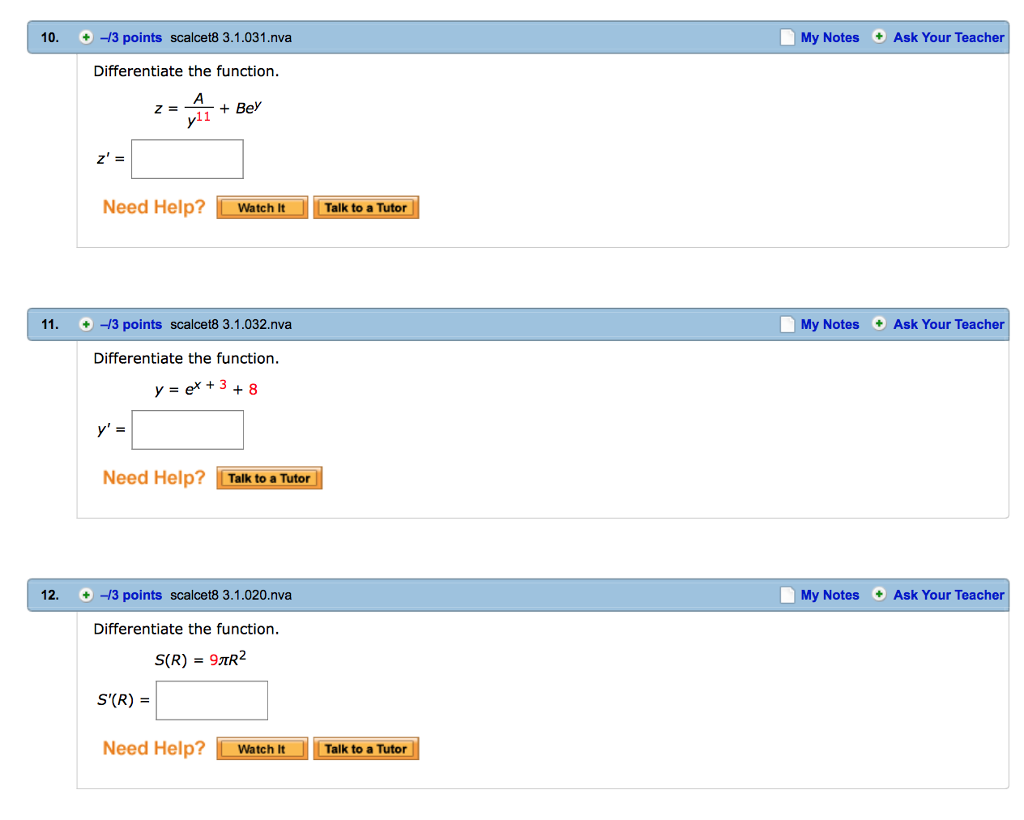



Differentiate The Function Z A Y 11 Be Y Z Chegg Com



3



Rolle S Theorem




Implicit Differentiation



6 Derivative Of The Exponential Function



6 Derivative Of The Exponential Function




Find The Derivative Of X Tan 1 X With Respect To X
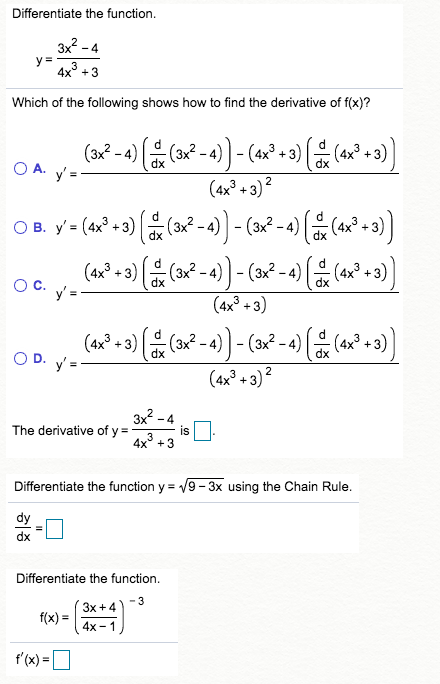



Differentiate The Function A Ve Which Of The Chegg Com




Worked Example Differentiating Related Functions Video Khan Academy




Ex 5 2 8 Differentiate Cos Root X With Respect To X




Misc 28 Find Derivative X 1 Tan X Chapter 13 Class 11



Inflection Points
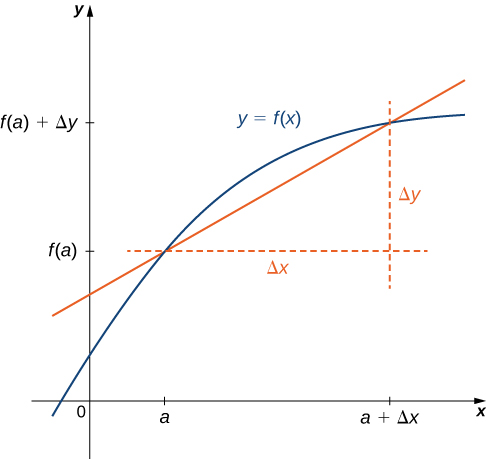



3 2 The Derivative As A Function Calculus Volume 1




Worked Example Differentiating Related Functions Video Khan Academy



Http Www Apsva Us Wp Content Uploads Legacy Assets Washingtonlee 3163bc16 Derivative Graph Notes Pdf



Derivatives Of Trigonometric Functions



The Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus



What Is The Differentiation Of Y X 7 X 2 X 3 Quora



Www Usna Edu Users Oceano Raylee Sm223 Ch14 5 Stewart 16 Pdf
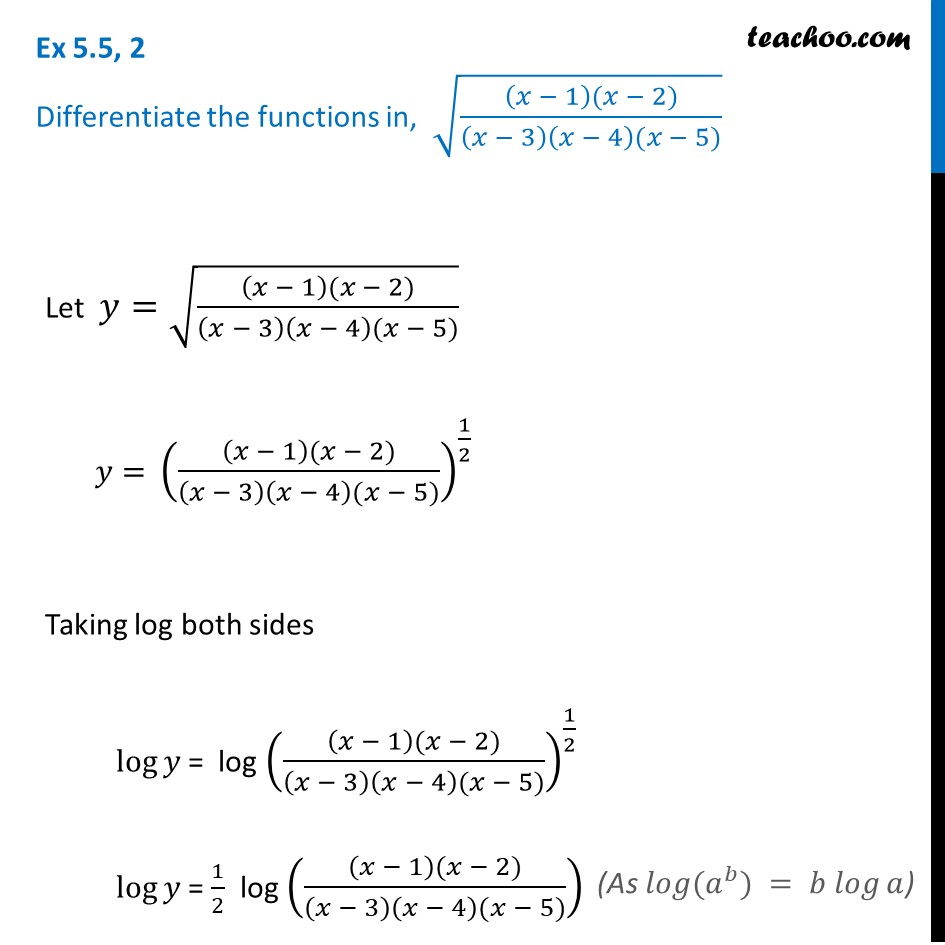



Ex 5 5 2 Differentiate Root X 1 X 2 X 3 X 4 X 5



Differentiate The Function H T 9 Squareroot T Chegg Com
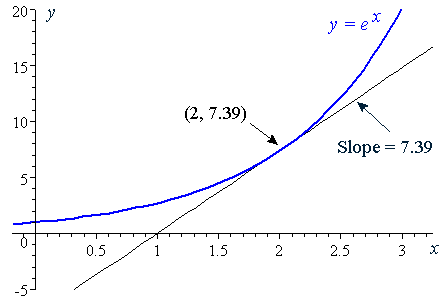



6 Derivative Of The Exponential Function



3 2 The Derivative As A Function Calculus Volume 1




Ex 6 2 8 Find X For Which Y X X 2 2 Is Increasing




Equation Of A Tangent To A Curve Differential Calculus Siyavula




14 5 The Chain Rule For Multivariable Functions Mathematics Libretexts
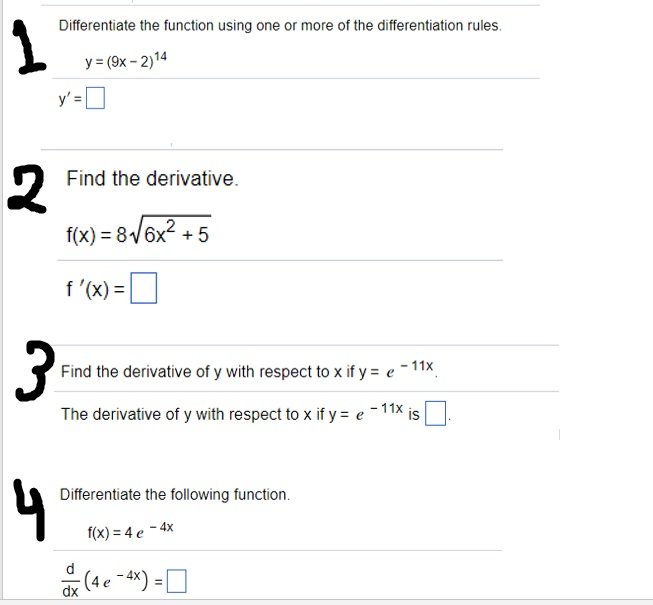



Differentiate The Function Using One Or More Of The Chegg Com




Finding Maxima And Minima Using Derivatives
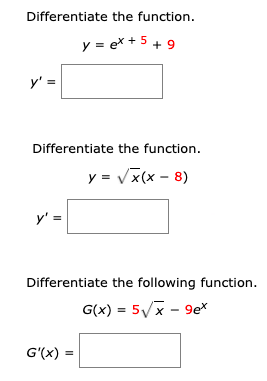



Differentiate The Function Y Ex 5 9 Y Chegg Com
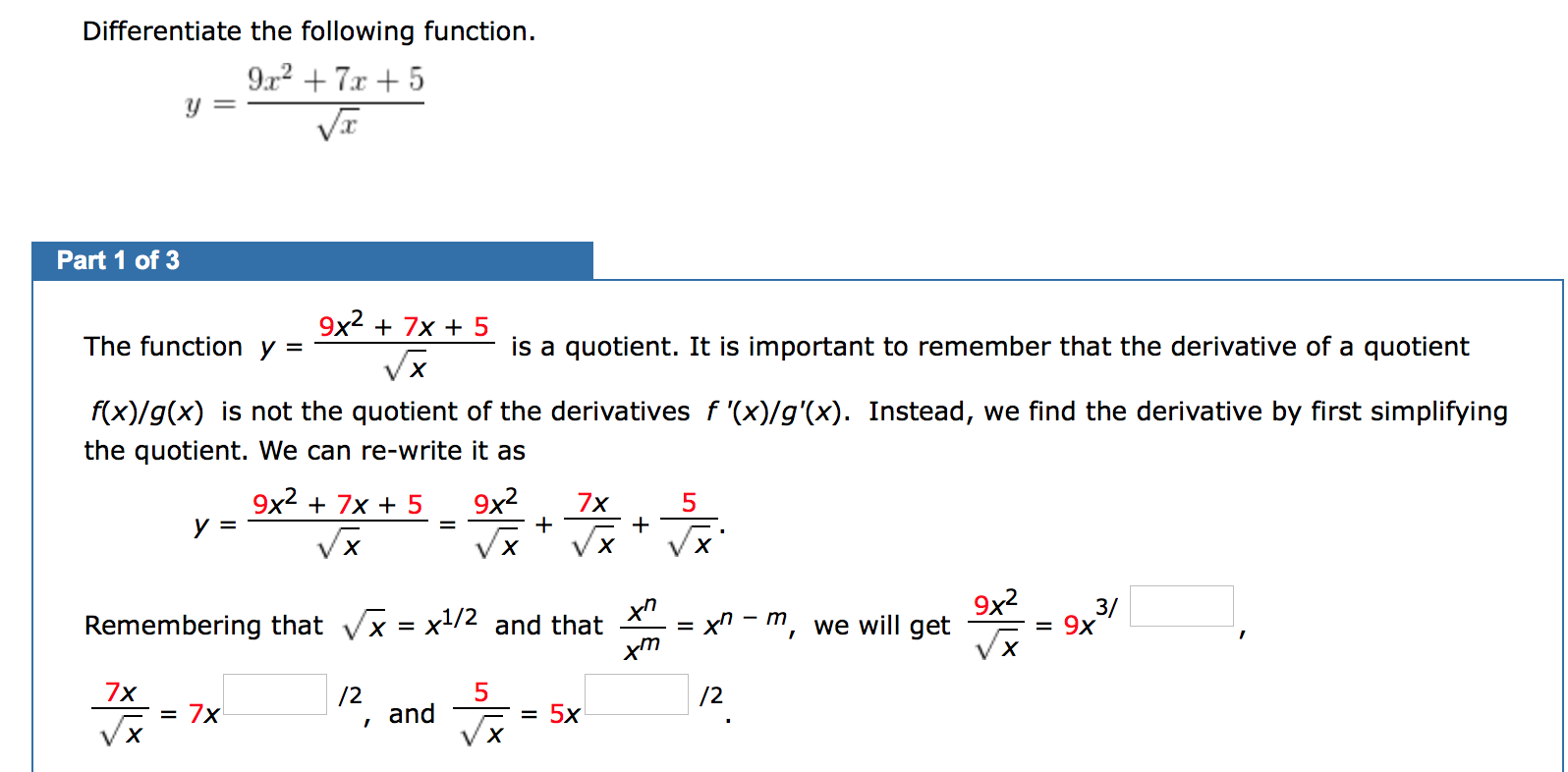



Differentiate The Following Function 9 R 7 0 5 Y Chegg Com




Derivatives Of Inverse Functions From Equation Video Khan Academy
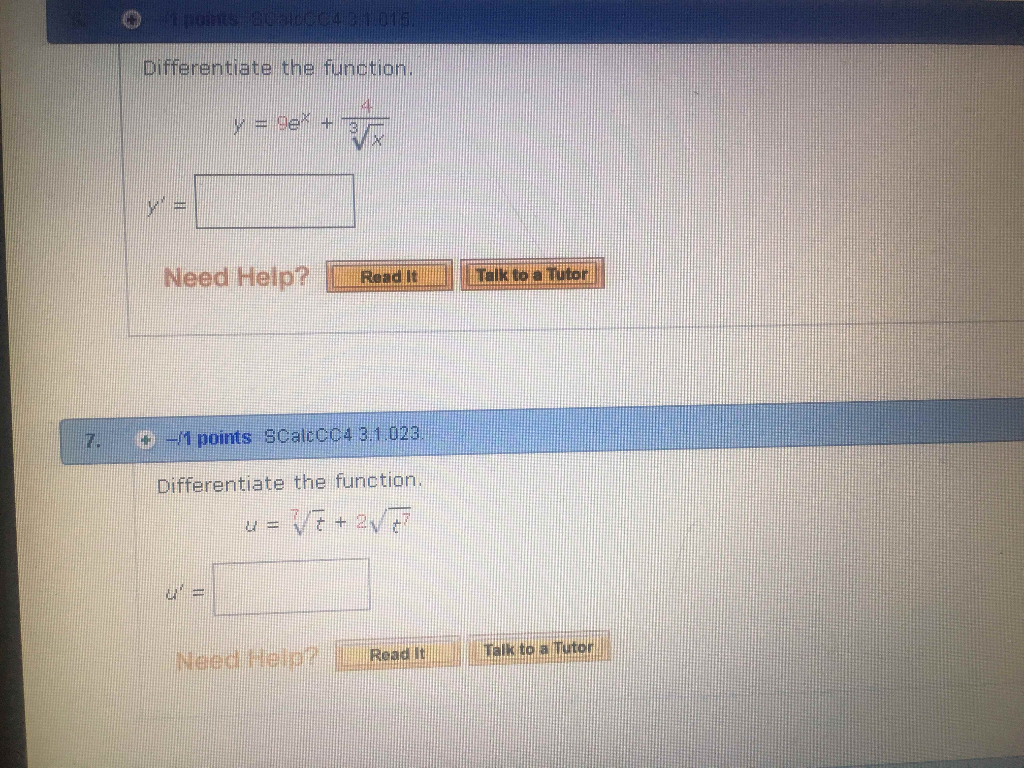



Differentiate The Function Y 9 E X 4 3 Chegg Com



3 The Derivative From First Principles




Differential Calculus Wikipedia
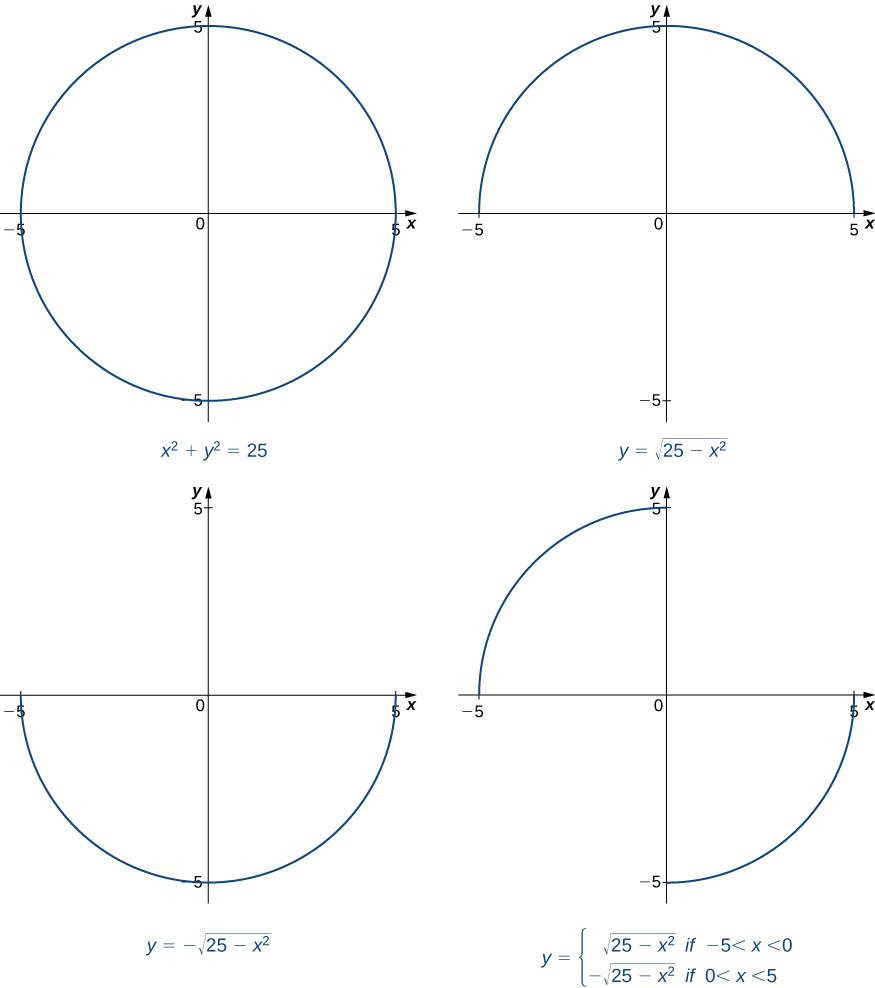



3 8 Implicit Differentiation Calculus Volume 1
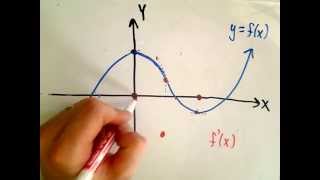



Sketching The Derivative Of A Function Youtube



Www Whitman Edu Mathematics Multivariable Multivariable 14 Partial Differentiation Pdf




Implicit Differentiation



Rolle S Theorem
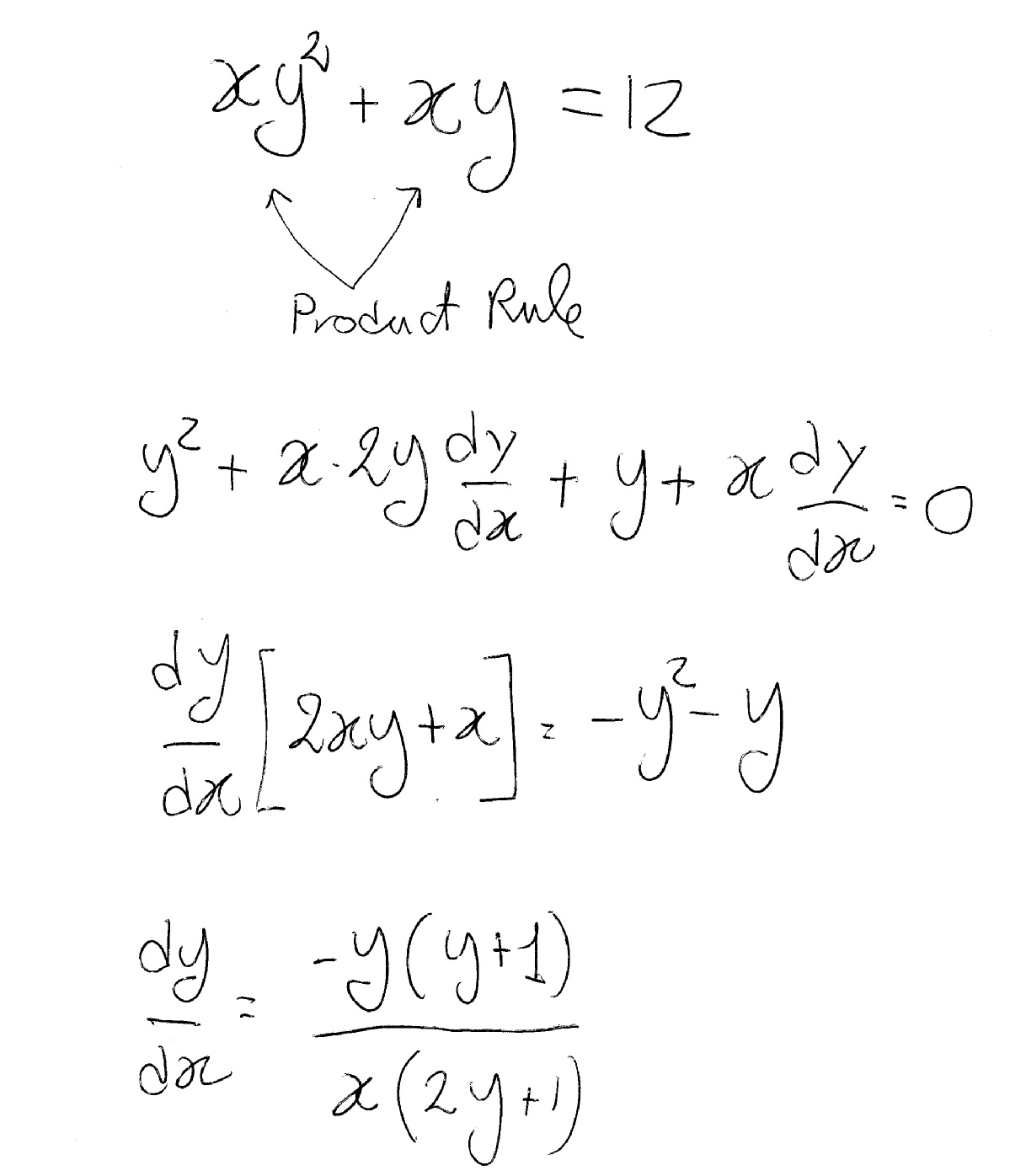



How Do You Differentiate Xy 2 Xy 12 Socratic




Differentiate Cos 1 Sqrt 1 Cosx 2 W R T X



3 8 Implicit Differentiation Calculus Volume 1




The Rate Of Change Of A Function



Curve Sketching




Derivative Wikipedia




Sketching Graphs Differential Calculus Siyavula
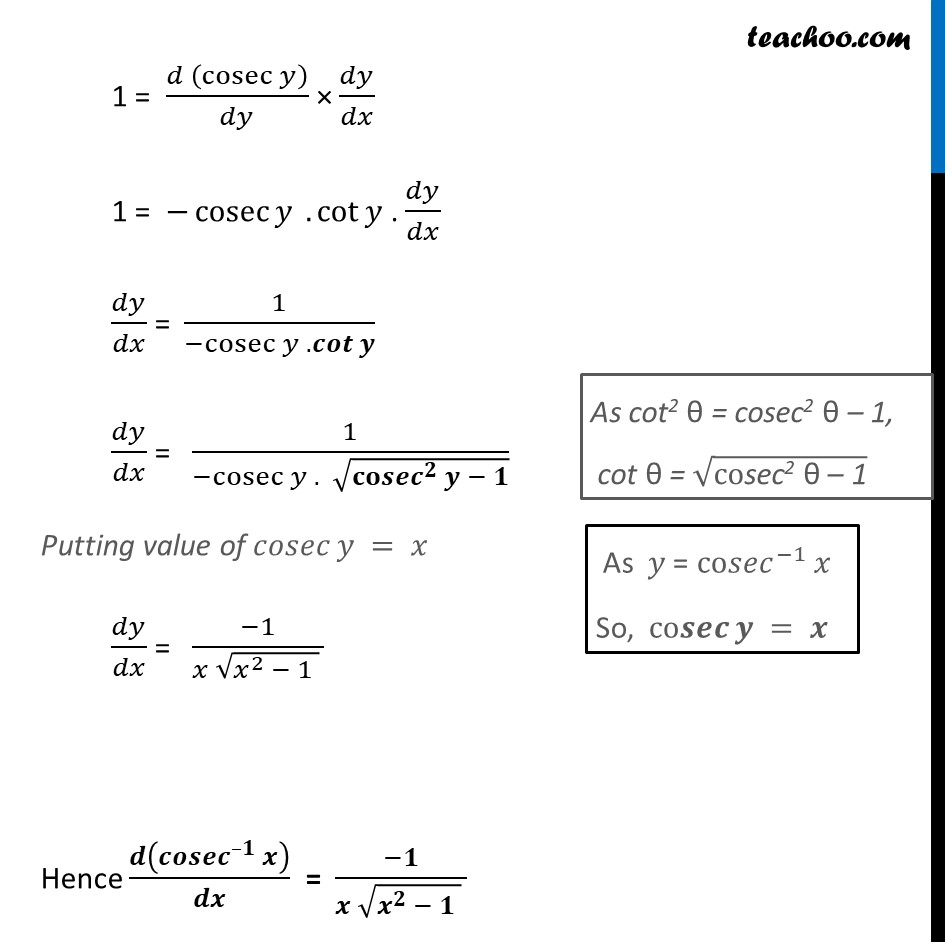



Derivative Of Cosec 1 X Cosec Inverse X Teachoo With Video




Differentiate Following Functions Y X 2 Pi 2 X Chegg Com



3 2 The Derivative As A Function Calculus Volume 1



What Is The Derivative Of 1 X Quora
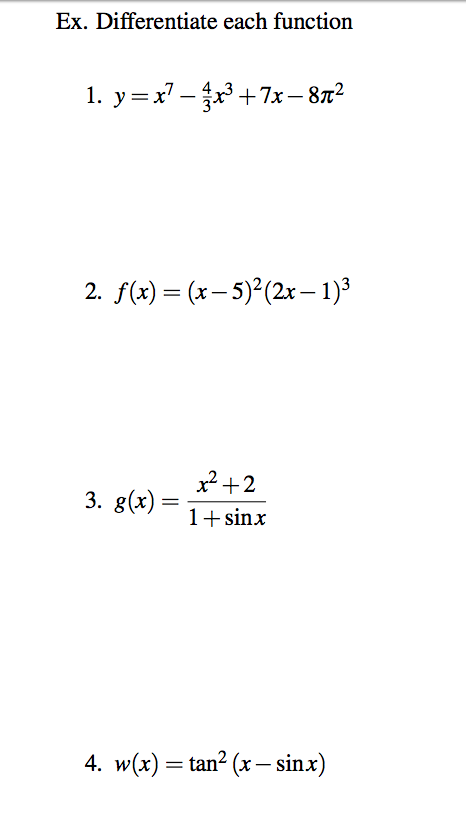



Differentiate Each Function Y X 7 4 3 X 3 7x Chegg Com




Ex 5 5 17 Differentiate Using Product Rule By Expanding Product




What Is The Derivative Of Log Y With Respect To X Mathematics Stack Exchange



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation



Derivative Of Square Root Youtube



Definition Of The Derivative
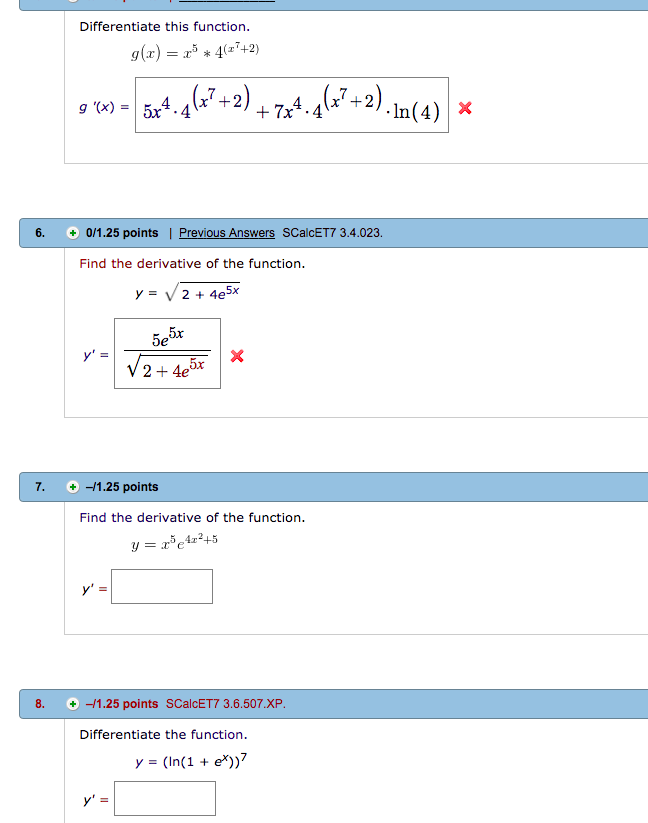



Differentiate This Function G Z 2 5 4042 Chegg Com




3 3 Differentiation Rules Mathematics Libretexts



Http Www Ed Ac Uk Files Atoms Files Week3 Answers Pdf
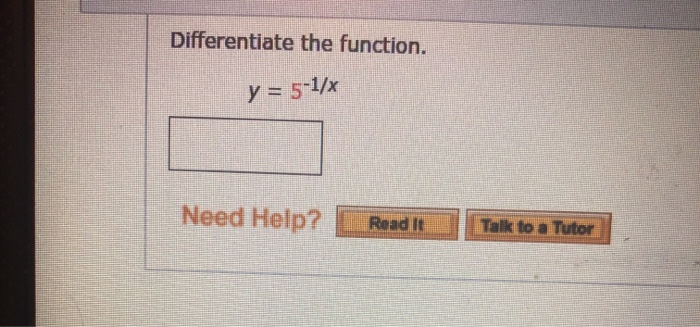



Solved Differentiate The Function Y 5 1 X Need Help R Chegg Com




Solutions To Implicit Differentiation Problems
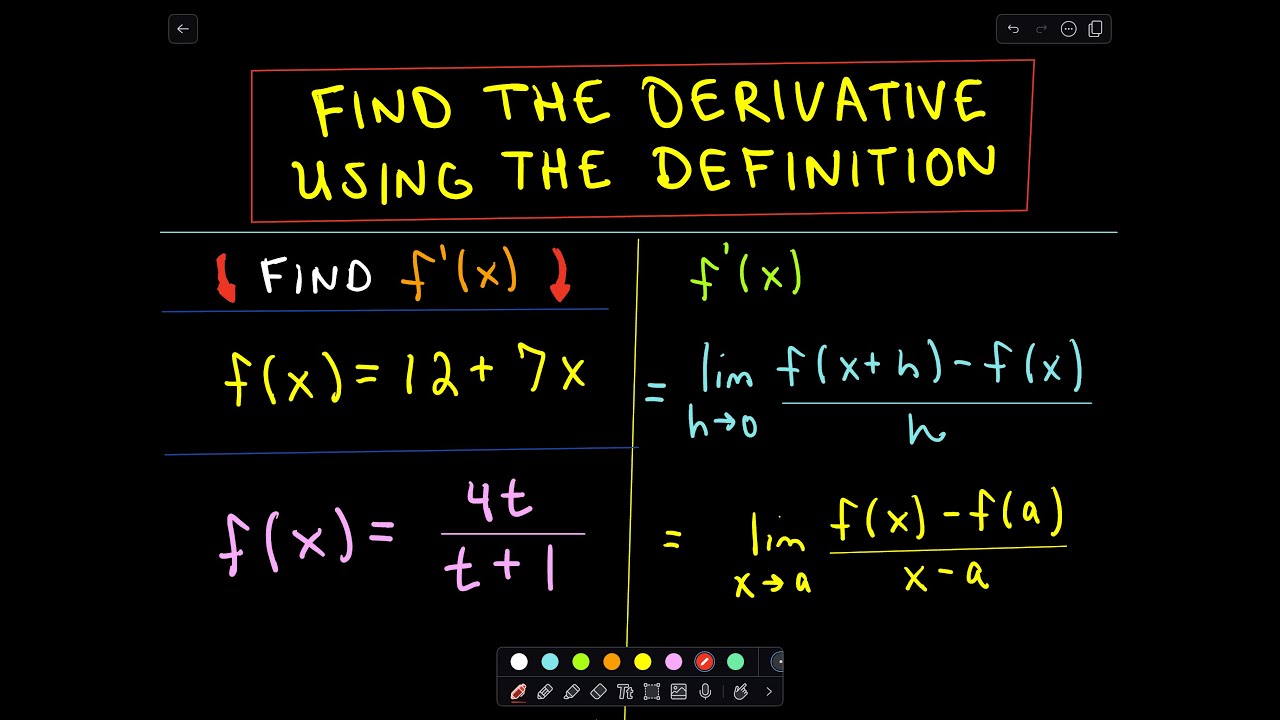



Finding A Derivative Using The Definition Of A Derivative Youtube
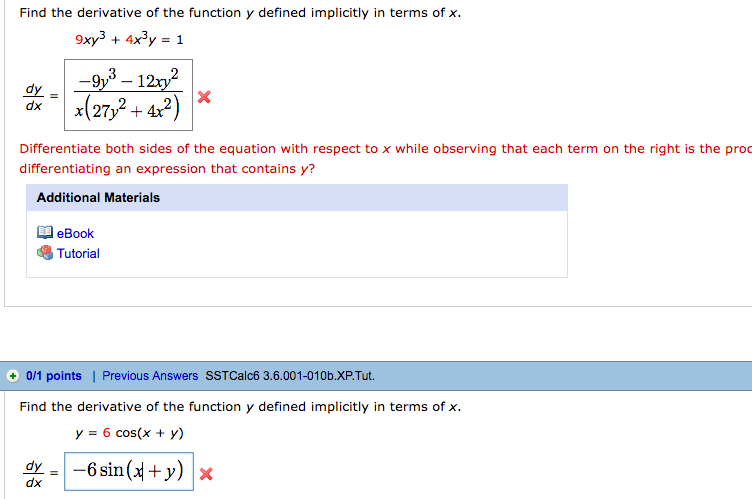



Find The Derivative Of The Function Y Defined Chegg Com
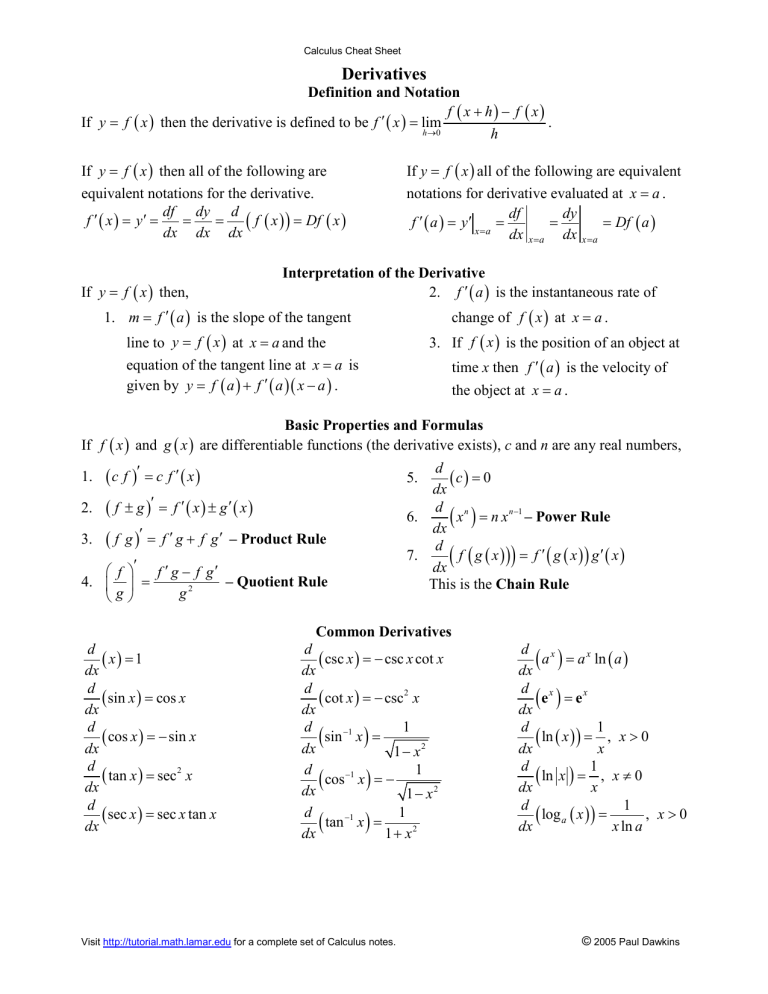



Calculus Cheat Sheet Derivatives



6 Derivative Of The Exponential Function



The Derivative Of A Constant With Examples Owlcation



3 8 Implicit Differentiation Calculus Volume 1


